You have likely been hearing and reading about high-availability (HA) everywhere and all the time, which is perhaps fitting for its name. This post will briefly talk about how DRBD® perfectly fits into a shared-nothing high-availability cluster.
The Shared-Nothing Architecture
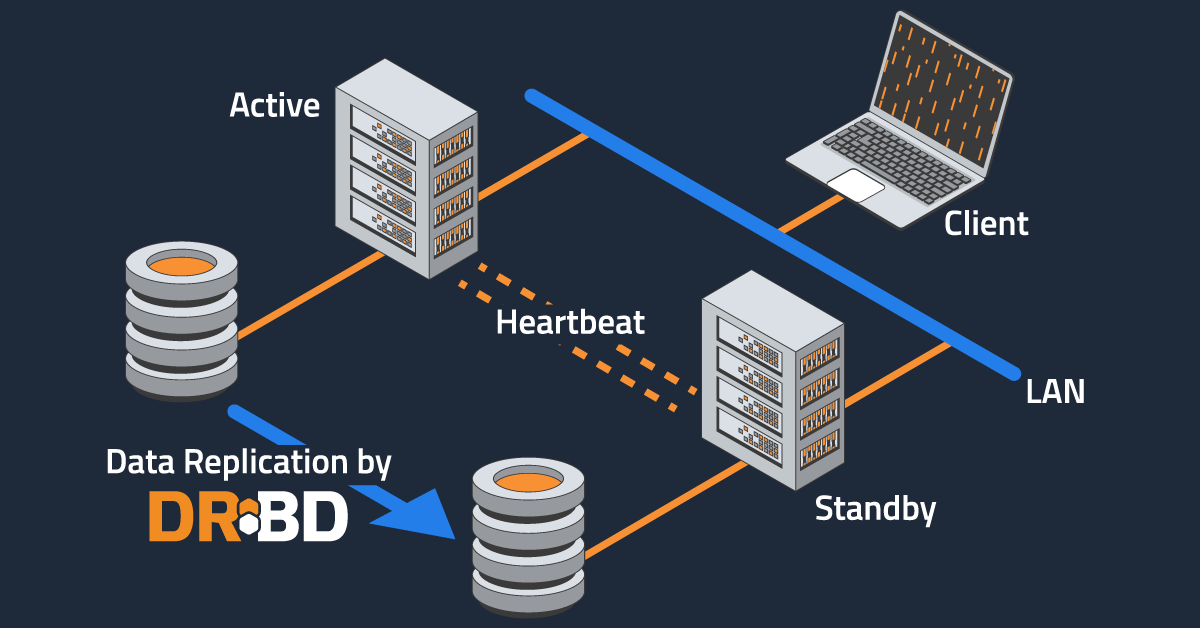
A shared-nothing architecture is normally based on two servers replicating data in real time with an automatic application failover in case of hardware or software failures on the active, or primary, server.
Because data is replicated across the servers in your cluster in real time, the recovery time objective (RTO) in a fail over is reduced to the time that it takes for your application to restart on the secondary server. This will usually happen in seconds.
The Flexibility & Cost Savings of a Shared-Nothing Solution
The shared nothing architecture has no hardware constraints. You can use physical or virtual servers, with any type of disks. You don’t need extra or dedicated hardware, and because you can use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) devices, there is no hardware vendor lock-in.
How DRBD Fits In
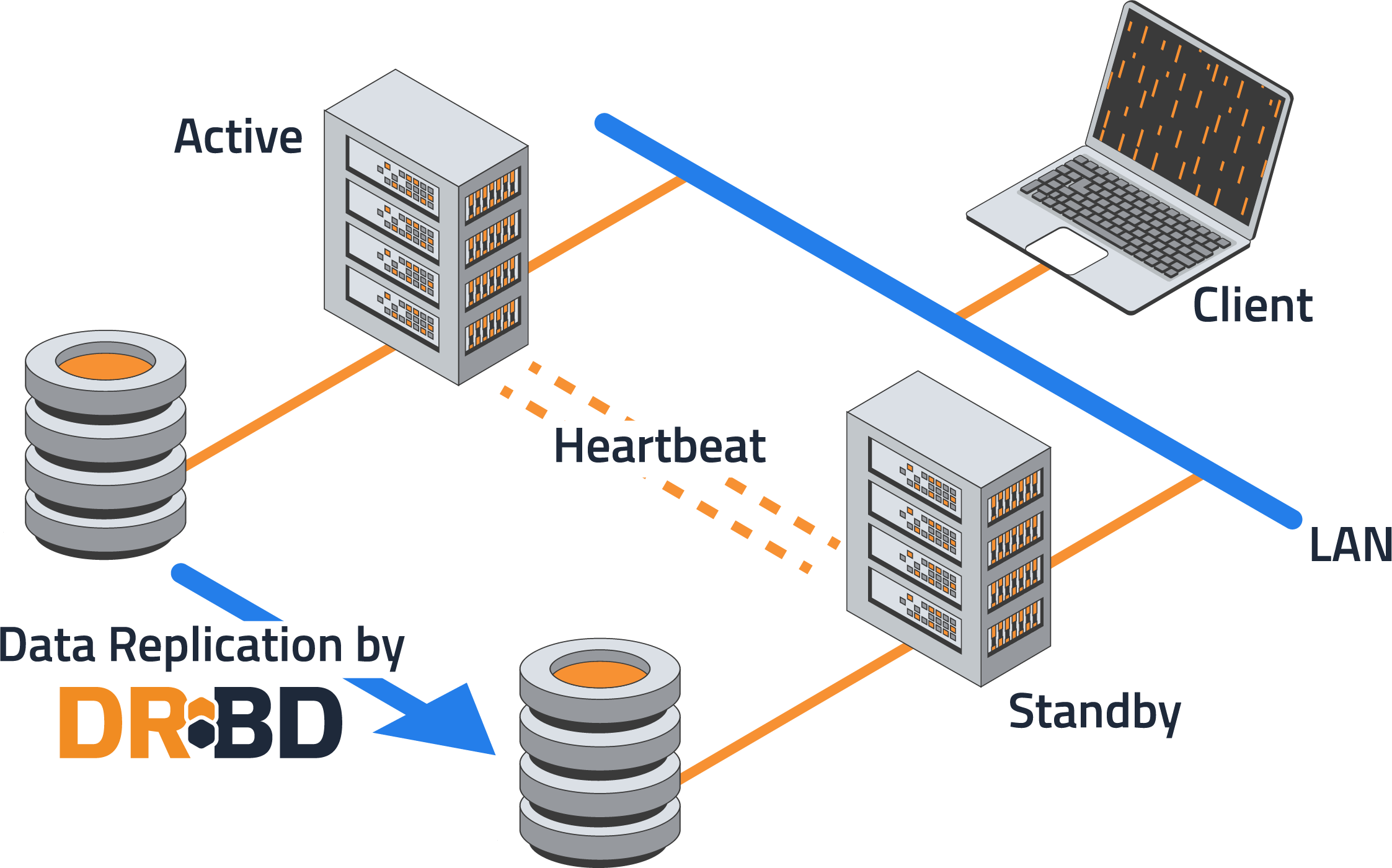
DRBD block replication in real time, also known as synchronous or Protocol C in DRBD-speak, is done between servers through standard network transport services, such as TCP/IP and RDMA.
LINBIT®, the creator and primary developer of DRBD for more than 20 years, also offers WinDRBD® for Microsoft Windows. WinDRBD is wire-compatible with DRBD v9. This means that you are no longer tied to using Linux servers and that you can even replicate your data in a mixed Windows and Linux environment.
The Total Solution
By leveraging a cluster resource manager, such as Pacemaker, and a cluster communication system, such as Corosync or Heartbeat, together with DRBD resources, you will have a total solution for a shared-nothing high-availability cluster.