LINBIT VSAN User Guide
1. Introduction
LINBIT VSAN is a software-defined storage solution for hyper-converged infrastructure, based on LINBIT’s DRBD and LINSTOR. It uses AlmaLinux 8 as a foundation and utilizes software by LINBIT to provide highly available storage to hypervisors through a convenient iSCSI target.
It is built primarily with VMware ESXi as a target platform in mind, but it is fully independent of the hypervisor software, so it should also work on any other virtualization platform.
| Please note that not all best practices recommended by LINBIT’s tech guides are implemented yet. For example, it is not yet possible to configure multiple links to separate application and replication traffic. |
2. Architecture
Logically, LINBIT VSAN fits inbetween the hypervisor and the virtual machines it provides storage for.

In practice, VSAN runs one of its instances as a virtual machine on each hypervisor in the cluster. The hypervisor passes its local storage through to VSAN, which then replicates the storage’s data across the cluster. One of the VSAN virtual machines exports an iSCSI target through a static IP. This iSCSI target can be fed back to the hypervisor in order to provide a highly available datastore. The resulting datastore can be used to store virtual machines and disk images on solid, redundant storage.
3. Prerequisites
Before you can start using LINBIT VSAN, you need a few things first:
-
LINBIT customer credentials, which are also used to log in to LINBIT’s Customer Portal. You can get these by requesting an evaluation.
-
A VSAN installation medium. You will receive a download link upon requesting an evaluation.
-
A virtualization platform, such as VMware ESXi.
-
Unrestricted internet access for all VSAN virtual machines.[1]
3.1. Number of Nodes
Because VSAN makes use of DRBD’s quorum mechanism, a VSAN cluster needs to consist of at least three member nodes.
The usual limitations and caveats of systems using quorum apply — for example, an odd number of nodes is greatly preferred over an even one. Please refer to the “Quorum” section of the DRBD 9 User Guide for more information.
4. Operating System Installation
LINBIT currently distributes VSAN in the following formats:
-
As an OVA image, for environments based on a VMware hypervisor.
-
As an ISO image, for solutions powered by any other hypervisor.
4.1. Installing via OVA file
This is the easiest method, geared towards users of a VMware hypervisor.
Take the following steps to set up your LINBIT VSAN cluster:
-
Import the OVA image into your VMware cluster. Make sure you create exactly one VSAN virtual machine on each hypervisor.
-
Pass through the local storage devices that should be used by VSAN for data replication.
Make sure the storage devices you pass through remain completely empty. For example, do not create any partitions or LVM volumes. -
Start all VSAN virtual machines. Because the image already contains a pre-baked operating system, you are done! Next, start the VSAN initialization process by navigating to the IP of one of your virtual machines using your browser.
| By default, the OVA image configures its network via DHCP. If you need more control (for example, a static IP or multiple addresses), you need to log into the VSAN virtual machine with the default credentials, and configure it directly using the stock operating system tools. |
|
When installing the operating system via the OVA image, a default password is set so that the machine can be administered over SSH. The default password for the Upon first login to a VSAN virtual machine, the user is prompted to change the default password. It is highly recommended to log into the machine over SSH and change the password immediately after installation. |
4.2. Installing via ISO file
This method is appropriate as a fall-back option for all non-VMware hypervisors that do not support importing OVA files. Of course, it can also be used on VMware hypervisors if greater flexibility in the operating system setup process is desired.
|
It is also possible to install LINBIT VSAN directly to physical machines, eliminating the need for any hypervisor software to be present at all. Since LINBIT VSAN is based on the AlmaLinux operating system, their guidelines for creating a physical installation medium apply. For a guide on how to write the LINBIT VSAN image to a physical medium, please refer to the AlmaLinux Wiki page on the subject. Simply use the LINBIT VSAN appliance image in place of the AlmaLinux image. |
Take the following steps to set up your LINBIT VSAN cluster:
-
Create one virtual machine for LINBIT VSAN on each hypervisor node.
-
Attach one virtual or local disk for the operating system itself.
-
Pass through the local storage devices that should be used by VSAN for data replication.
Make sure the storage devices you pass through remain completely empty. For example, do not create any partitions or LVM volumes. -
Assign at least one network adapter to each of the virtual machines. VSAN acquires an IP address via DHCP.
-
Start the virtual machines and complete the operating system setup on each machine. This is similar to a regular AlmaLinux 8 installation process.
Do not use a kickstart file to automate the installation process. The VSAN ISO already contains a kickstart file to customize certain aspects of the AlmaLinux 8 installer; providing an additional kickstart file will cause conflicts. Make sure you take note of the special requirements regarding Networking and Time during the setup process. -
Done! Next, start the VSAN initialization process by navigating to the IP of one of your virtual machines using your browser.
4.2.1. Networking
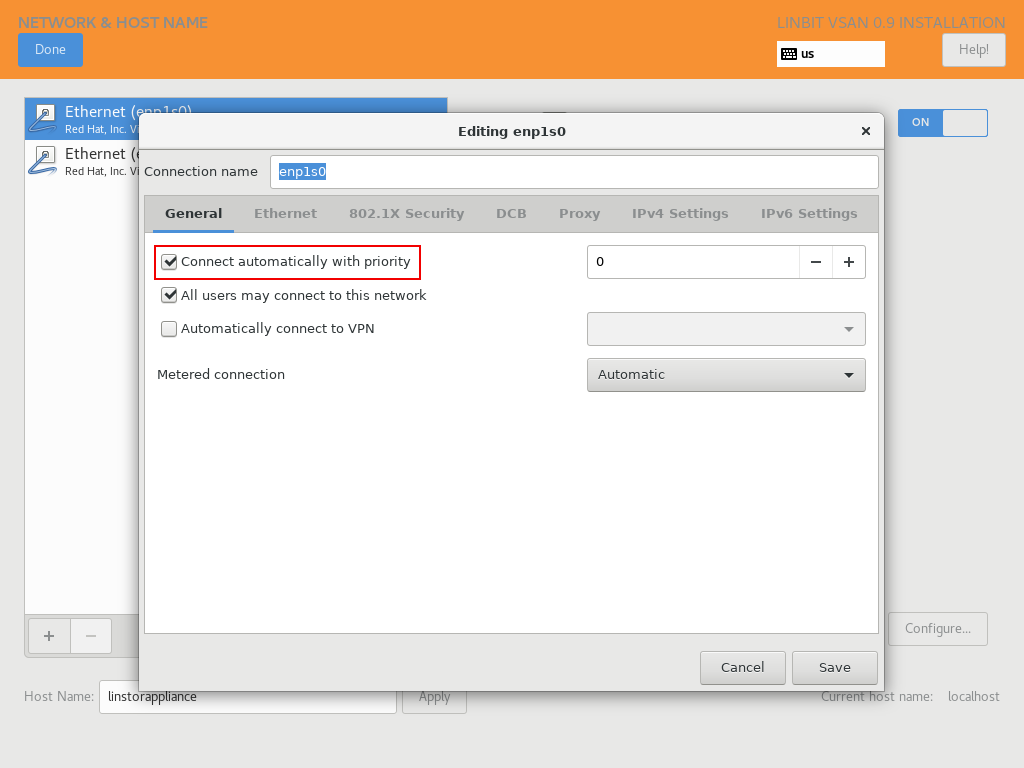
VSAN relies on a network connection being made available on boot. By default, the AlmaLinux installer configures the network interface to not automatically connect.
Please make sure that, when configuring the network interface, the “Connect automatically with priority” checkbox is checked.
4.2.2. Time
In a cluster of multiple servers, it is important to ensure that the clocks of the individual nodes are in sync with each other.
This is easiest achieved by using NTP (Network Time Protocol). Please make sure that NTP is enabled in the AlmaLinux setup and that the nodes’ clocks are synchronized after the installation is done.
5. Initialization
After the operating system is installed and all VSAN virtual machines are booted, you can proceed to set up your VSAN cluster.
|
To ensure the setup experience is as smooth as possible, make sure you meet the following requirements before starting the initialization process:
|
To get started, navigate to the IP address of one VSAN virtual machine with your browser.
If you are not sure what the IP address of your virtual machine is, refer to the helpful message VSAN prints to the console and when logging in over SSH:
Welcome to LINBIT VSAN version 0.9.12 Please visit the following URL in your browser to start the setup process: https://192.168.122.190:443 Last login: Mon May 10 14:26:07 2021 from 192.168.122.1 [root@uninitialized-2704efc50652198ea06592f8 ~]#
VSAN gives you a one-stop Web UI wizard to configure the storage cluster. Follow the instructions in the wizard to complete the installation.
Step by step screenshots can be found on LINBIT’s website, and there is also a walk-through video.
| For general help with the terms and concepts used during the setup, refer to the LINSTOR User Guide. |
6. Administration
The VSAN Web UI intenionally offers relatively minimal administration and monitoring capabilities.
One of VSAN’s design philosophies is that, after the setup is completed, it should be as close to a regular Linux system as possible.
So, if you are familiar with the technologies under the hood, you are free to directly use the underlying operating system and treat it as a standard AlmaLinux-based LINSTOR cluster.